Airfield Urbanism
“
— ”
There are about 8 places in Berlin that were or have been used as an airfield, one of the significant examples is Tempelhof Flughafen. Before Flughafen Berlin-Tempelhof was built the area was called ‘Tempelhofer Feld.’ It has been used as farm land, 32 sports fields, military training grounds, and location for many entertainment activities. The airport was established in 1923 - in 1926, Deutsche Lufthansa was founded on Tempelhofer Feld, and the first airport building was completed in 1928.
During the Berlin Blockade period in 1948-1949, the airport played an important role supplying West Berlin, becoming the symbol of the defense of freedom as an airport of the U.S. Air Force. The history of the Tempelhof field also provides an insight into the ideology and reality of the National Socialist regime. The premises were a stage for propagandistic mass rallies and a location for the only official Berlin concentration camp. The new airport building with its characteristic features of NS architecture was used for arms production and forced labor during the Second World War.
Nowadays many airports in Berlin have been transformed to solar parks or other industrial use but the multiple historical layers in Tempelhof Flughafen makes it become more valuable for citizens. Since its closure in 2008, the immense expanse has been used as a city park and for a wide range of activities, ranging from sports, barbecue area, allotments, playing field, hiking area, sunbathing area, kite field and nature education by elementary schools. There are also major activities taking place, such as parts of Berlin Fashion Week, concerts and the annual Berlin Festival. Berlin has now been enriched by one of the largest urban open spaces in the world with international appeal. There are now over 300 hectares of green in this big park.
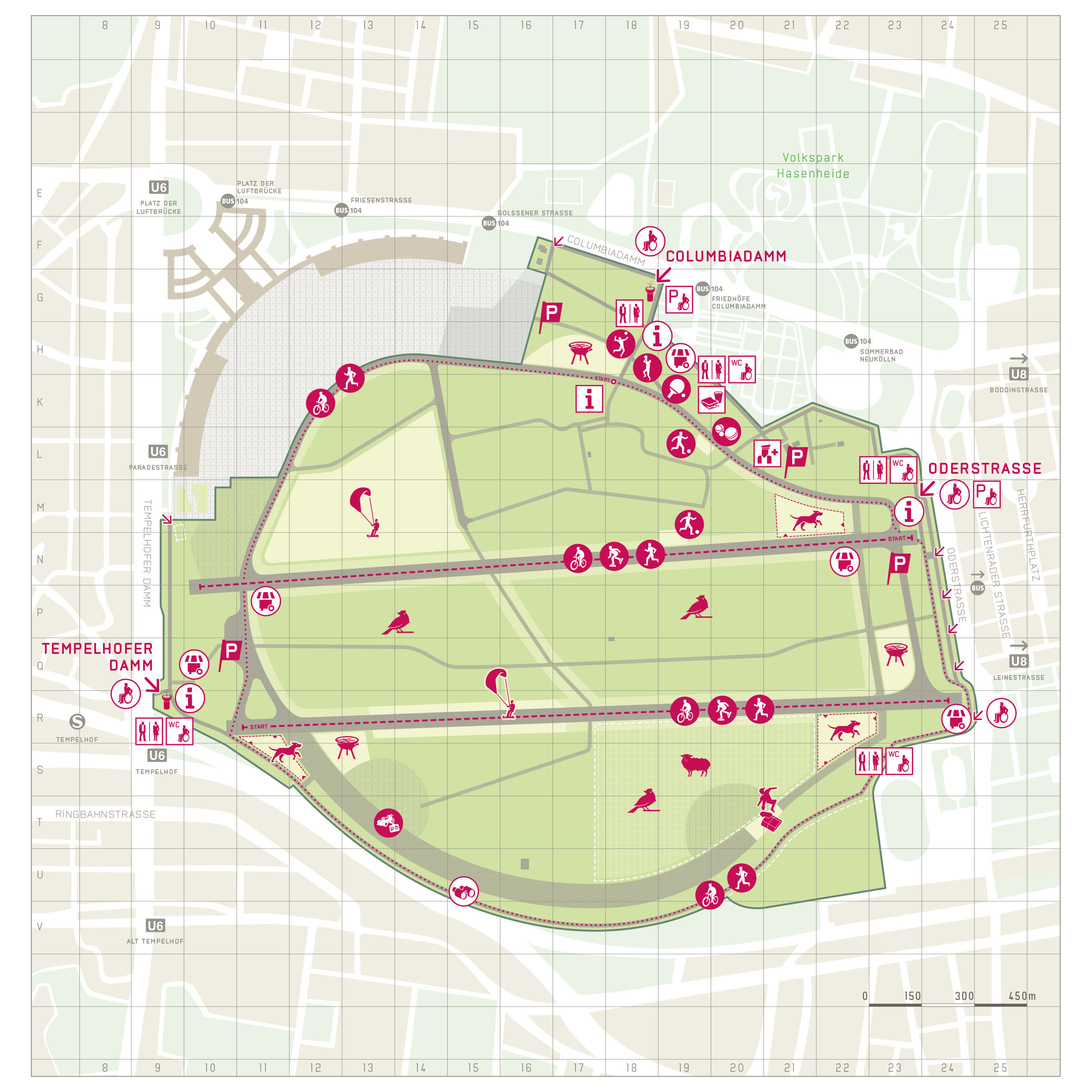
Image source: “About the Park.” Accessed March 6, 2022. https://gruen-berlin.de/en/projects/parks/tempelhofer-feld/about-the-park.
References
1. “Forgotten Airfields Europe.” Accessed March 6, 2022. https://forgottenairfields.com/detailcountry.php?categoryId=268.
2. “Berlin Tempelhof Airfield until 1945.” Accessed March 6, 2022. https://www.mil-airfields.de/germany/berlin-tempelhof-airfield.htm.
1. “Forgotten Airfields Europe.” Accessed March 6, 2022. https://forgottenairfields.com/detailcountry.php?categoryId=268.
2. “Berlin Tempelhof Airfield until 1945.” Accessed March 6, 2022. https://www.mil-airfields.de/germany/berlin-tempelhof-airfield.htm.